The Art of Fermentation: Probiotic-Rich Recipes for Gut Health
Welcome to “The Art of Fermentation: Probiotic-Rich Recipes for Gut Health.” In recent years, there has been a growing recognition of the vital role gut health plays in our overall well-being. At the heart of maintaining a healthy gut lies the power of probiotics – beneficial bacteria that promote digestion, boost immune function, and support mental health. And one of the most ancient and revered methods of harnessing the power of probiotics is through fermentation. This article dives into the fascinating world of fermentation, exploring its history, importance, and providing you with a collection of delicious, probiotic-rich recipes to enhance your gut health. Whether you are new to fermentation or an experienced fermenter looking for inspiration, this guide will equip you with the knowledge and techniques to embark on your own fermentation journey.
1. Introduction to the Art of Fermentation
Why Fermentation is Essential for Gut Health
We all know that maintaining good gut health is crucial for overall well-being. And one powerful way to promote a flourishing gut is through fermentation. Fermentation is the magical process in which microorganisms, like bacteria and yeast, break down sugars and transform them into organic acids or alcohol. This not only enhances the flavor and texture of food but also creates a rich source of probiotics – the friendly bacteria that support digestion and boost our immune system.
The History and Cultural Significance of Fermentation
Fermentation has been a part of human food culture for thousands of years. From ancient civilizations to modern societies, fermentation has played a vital role in preserving food and adding complex flavors to our culinary traditions. Think sauerkraut from Germany, kimchi from Korea, or miso from Japan. Each culture has its own unique fermentation practices, and these traditions have been passed down through generations, celebrating the art of preserving food while benefiting our gut health.
2. Understanding the Importance of Probiotics for Gut Health

What Are Probiotics and Why Do We Need Them?
Probiotics are live microorganisms that, when consumed in adequate amounts, provide health benefits to the host. In simpler terms, they are the good guys that help maintain balance in our gut. Our gut is home to trillions of microorganisms, both beneficial and harmful. Probiotics help crowd out the bad bacteria, reducing the risk of digestive issues, enhancing nutrient absorption, and even improving mental health.
The Role of Probiotics in Maintaining a Healthy Gut
A healthy gut is like a well-orchestrated symphony. Probiotics play a pivotal role in maintaining this harmony. They support the production of enzymes that help break down food and aid in nutrient absorption. They also strengthen the gut lining, preventing harmful substances from entering the bloodstream. Additionally, probiotics stimulate the immune system, making it more resilient to infections and allergies. So, by incorporating probiotics into our diet, we’re actively nourishing our gut and supporting overall well-being.
3. Getting Started: Essential Tools and Ingredients for Fermentation
Must-Have Fermentation Equipment
Ready to dive into the world of fermentation? You’ll need a few essential tools to get started. First, invest in high-quality fermentation vessels like glass jars or ceramic crocks. These containers should be airtight to create an oxygen-free environment for fermentation. You’ll also need airlocks, which allow carbon dioxide produced during fermentation to escape while keeping out unwanted contaminants. Lastly, make sure you have a reliable fermentation weight to keep your ingredients submerged in their brine.
Choosing the Right Ingredients for Successful Fermentation
When it comes to fermentation, the quality of ingredients is paramount. Opt for organic, fresh produce to ensure you’re not introducing harmful pesticides or preservatives into the fermentation process. Vegetables like cabbage, cucumbers, and radishes are excellent choices for fermenting. Herbs and spices can also add a wonderful depth of flavor. And don’t forget the salt! It not only adds taste but also helps create the ideal conditions for fermentation by inhibiting the growth of undesirable bacteria.
4. Exploring Probiotic-rich Fermented Foods and Beverages

Sauerkraut: The Classic Fermented Vegetable
Ah, sauerkraut, the quintessential fermented cabbage. This classic German delicacy is not only packed with probiotics but also bursts with tangy and crunchy goodness. Enjoy it as a side dish, on sandwiches, or even as a topping for hot dogs. Pro tip: experiment by adding caraway seeds or grated carrots for an exciting twist.
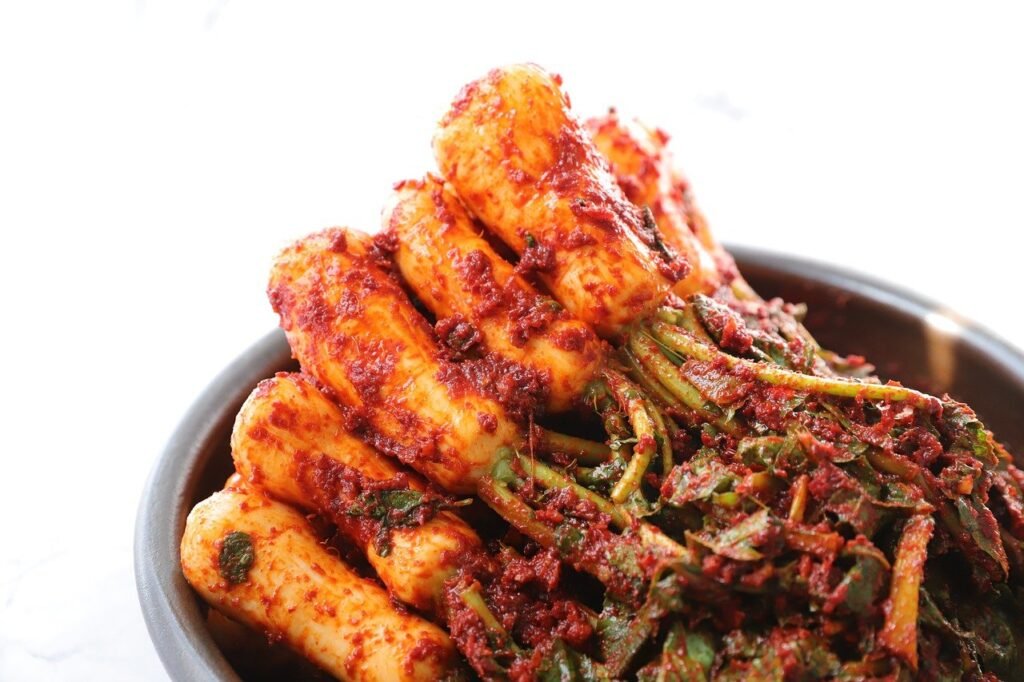
Kimchi: The Spicy Korean Fermented Delight
Kimchi, a staple in Korean cuisine, is a fiery and tangy blend of fermented vegetables, often featuring cabbage, radishes, and scallions. Bursting with bold flavors and a kick of heat, kimchi will add a zing to any meal. Try it as a side dish, a topping for rice bowls, or as a secret ingredient in your homemade stir-fries.
Miso: A Staple in Japanese Cuisine
Miso, a traditional Japanese seasoning, is made by fermenting soybeans with salt and a special koji culture. This umami-rich paste adds depth of flavor to soups, marinades, and dressings. Start with a mild white miso and gradually explore the diverse range of flavors, from nutty red miso to robust barley miso.
Tempeh: A Nutrient-Dense Fermented Soy Product
Tempeh is a versatile and protein-packed fermented soy food originating from Indonesia. With its firm texture and nutty flavor, tempeh can be grilled, baked, or stir-fried to create delicious plant-based dishes. Crumble it into salads, marinate it for sandwiches, or use it as a meat substitute in tacos—a truly delectable addition to any diet.
Yogurt: The Creamy Probiotic Powerhouse
Who doesn’t love yogurt? This creamy and tangy delight is created by fermenting milk with live bacterial cultures. A fantastic source of probiotics, yogurt can be enjoyed plain, mixed with fruits and granola, or used as a base for smoothies and salad dressings. Explore the world of Greek yogurt, Icelandic skyr, or dairy-free alternatives for a gut-healing treat.
Other Probiotic-rich Foods and Beverages to Try
The world of fermentation is vast, and there are countless probiotic-rich foods and beverages to explore. Kombucha, a fizzy fermented tea, is a popular choice, offering a refreshing and tangy taste. Kefir, a fermented milk drink, provides a probiotic punch in every sip. And don’t forget about pickles, sourdough bread, and even some cheeses, which also undergo fermentation processes that contribute to gut health. Let your adventurous spirit guide you through this flavorful and beneficial journey.

Now that you have a taste of the art of fermentation and the wonders of probiotics, it’s time to embrace this ancient tradition and start bringing gut-friendly, flavorful creations into your own kitchen. Get ready to nourish your gut, tantalize your taste buds, and embark on an exciting culinary adventure that will leave you feeling vibrant and alive. Cheers to fermentation and a happy gut!Almond, and Cashew Delights
5. Step-by-Step Guide: Fermenting Vegetables for Optimal Gut Health
Preparing Vegetables for Fermentation
Fermenting vegetables might sound fancy, but it’s actually a simple process that anyone can do at home. To get started, you’ll need some fresh vegetables of your choice. Wash them thoroughly and cut them into the desired size and shape. Don’t be afraid to get creative with your vegetable combinations! From classic sauerkraut to spicy kimchi, the possibilities are endless.
Choosing the Right Salt and Brine Ratio
Salt plays a crucial role in the fermentation process, as it helps create an environment that promotes the growth of good bacteria while inhibiting the growth of harmful bacteria. When fermenting vegetables, you’ll need to create a brine by dissolving salt in water. It’s important to use the right salt-to-water ratio to ensure the fermentation process goes smoothly. A general rule of thumb is to use about 1-2% salt by weight, depending on your personal taste preferences.
Packaging and Fermenting Vegetables
Once your vegetables are prepared and your brine is ready, it’s time to pack them into a fermentation vessel. You can use glass jars, ceramic crocks, or specially designed fermentation kits. The key is to make sure the vegetables are fully submerged in the brine to prevent the growth of mold or other unwanted bacteria. You can use weights or even a plastic bag filled with brine to keep the vegetables submerged.
Monitoring and Troubleshooting the Fermentation Process
After sealing the fermentation vessel, it’s important to keep an eye on your fermenting vegetables. Fermentation is an active process, and you may notice bubbles or a slightly sour smell, which is completely normal. However, if you see any signs of mold or an off-putting odor, it’s best to discard the batch and start fresh. Remember, fermentation is a natural process and not an exact science, so don’t be too hard on yourself if you encounter any hiccups along the way.

6. Unleashing the Power of Kombucha and Kefir: Fermented Drinks for Gut Healing
Kombucha: Brewing Your Own Probiotic-rich Tea
Move over, soda! Kombucha is a fermented tea that not only satisfies your thirst but also supports a healthy gut. If you’re feeling adventurous and want to try brewing your own kombucha, all you need is a SCOBY (symbiotic culture of bacteria and yeast), tea, sugar, and patience. Let the SCOBY work its magic as it transforms sweet tea into a tangy, effervescent drink packed with beneficial bacteria. Cheers to gut health!
Kefir: A Creamy and Tangy Fermented Beverage
Looking for a creamy and tangy alternative to yogurt? Meet kefir! This probiotic-rich drink is made by adding kefir grains to milk, which undergoes a fermentation process lasting anywhere from 24 hours to a couple of days. The result is a slightly fizzy, tangy beverage that can be enjoyed on its own, blended into smoothies, or poured over granola. And the best part? You can make your own kefir right in the comfort of your kitchen.
Other Fermented Drinks to Enhance Gut Health
In addition to kombucha and kefir, there are plenty of other fermented drinks that can provide a boost of probiotics to your gut. From kvass, a traditional Russian beverage made from fermented vegetables, to ginger beer, a spicy and refreshing soda alternative, there’s something for everyone. Don’t be afraid to explore the world of fermented beverages and find your own favorite gut-healing elixir.
7. Probiotic Treats: Fermented Dairy and Non-Dairy Products for Gut Health
Fermented Dairy Products: Yogurt, Cheese, and Beyond
Dairy lovers, rejoice! Fermenting dairy products not only enhances their flavors but also increases their probiotic content. Yogurt, with its creamy texture and tangy taste, is a classic example of a fermented dairy product. But why stop there? You can also try your hand at making homemade cheese or even experiment with fermented butter. The possibilities are as endless as the flavors you can create.
Fermented Non-Dairy Alternatives: Coconut, Almond, and Cashew Delights
For those who prefer a non-dairy approach, fear not! You can still enjoy the benefits of fermentation with plant-based alternatives. Coconut milk, almond milk, and cashew milk are just a few options that can be transformed into creamy, probiotic-rich treats. Whether you fancy a spoonful of coconut yogurt or a glass of almond milk kefir, there’s no shortage of delicious possibilities to satisfy your gut and your taste buds.
Getting Creative with Fermented Treats
Fermentation doesn’t have to stop at traditional dairy or non-dairy products. Get adventurous and explore the world of fermented delights! From fermented salsa and pickles to tangy hot sauce and even probiotic-packed chocolate, there’s a whole realm of possibilities to experiment with. Don’t be afraid to let your creativity run wild and discover unique and delicious ways to incorporate fermented treats into your life.
8. The Fermented Pantry: Incorporating Probiotic-Rich Foods into Everyday Cooking

Adding Fermented Condiments to Your Meals
Elevate your meals with the magic of fermented condiments. Sauerkraut, kimchi, and pickles are not only delicious on their own but also make wonderful additions to sandwiches, salads, and tacos. The tangy, probiotic-packed flavors can bring a new dimension to your favorite dishes and help support a happy, healthy gut.
Using Fermented Ingredients in Sauces and Dressings
Sauces and dressings are the perfect canvas for adding fermented ingredients. Whether you’re making a tangy vinaigrette with fermented apple cider vinegar or a creamy dressing with fermented miso paste, the possibilities are mouthwatering. Experiment with different combinations and let your taste buds guide you to flavor nirvana.
Experimenting with Fermented Flavors
Fermentation opens up a whole new world of flavors to explore. From the deep umami of fermented soybean paste to the tangy punch of fermented hot peppers, there’s something for every palate. Incorporate fermented flavors into your cooking by adding a spoonful of miso to your soup, a splash
As you conclude your journey into the art of fermentation, we hope this article has provided you with a solid foundation to explore the world of probiotic-rich foods and beverages. By incorporating these delicious and nourishing creations into your diet, you can support your gut health and overall well-being. Remember, fermentation is a process that requires patience and experimentation, so don’t be afraid to try new recipes and adjust techniques to suit your taste preferences. Embrace the art of fermentation and enjoy the benefits of a happy, healthy gut!
FAQ
1. Is fermentation safe for consumption?
Yes, fermentation is generally safe for consumption when done properly. The process of fermentation creates an acidic environment that inhibits the growth of harmful bacteria. However, it is important to follow proper hygiene practices, use clean equipment, and ensure that the fermentation process occurs at the correct temperature to prevent any potential risks.
2. Can I ferment foods and beverages at home without any specialized equipment?
Absolutely! While specialized equipment can make the fermentation process more convenient, it is not always necessary. Many fermentation recipes can be done using basic kitchen tools such as mason jars, fermentation weights, and cheesecloths. However, if you plan to ferment on a larger scale or experiment with more complex recipes, investing in specific fermentation equipment may be beneficial.
3. How long does the fermentation process typically take?
The length of fermentation can vary depending on the recipe and the desired flavor and texture. Some ferments may be ready in a few days, while others may take several weeks or even months. It is important to taste-test your ferments regularly to determine when they have reached the desired level of acidity and flavor. Remember, the temperature and environment in which you ferment can also impact the fermentation time.
4. Can I consume fermented foods and beverages if I am lactose intolerant or have dietary restrictions?
Yes, there are many fermented foods and beverages that are suitable for lactose intolerant individuals or those with dietary restrictions. For example, lactose is often consumed by the beneficial bacteria during fermentation, making many fermented dairy products, such as yogurt and kefir, more easily digestible for those with lactose intolerance. Additionally, there are numerous non-dairy alternatives, such as fermented vegetables, kombucha, and water kefir, that provide probiotic benefits without any dairy content.